Are you struggling with eczema and wondering what exactly qualifies as severe? Look no further! In this article, we will explore the criteria for determining the severity of eczema so that you can better understand your condition and seek appropriate treatment. From persistent itching to extensive skin inflammation, we will cover all the key factors that medical professionals consider when diagnosing severe eczema. So, whether you’re personally affected or seeking knowledge to support a loved one, this article will provide valuable insights into what counts as severe eczema.
What Counts As Severe Eczema?
Understanding Eczema
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflamed, itchy, and red patches of skin that can be very uncomfortable and even debilitating. Eczema is often associated with several symptoms, but it can vary in severity from person to person. Understanding the different levels of severity is crucial in managing and treating the condition effectively.
Normal Eczema Symptoms
In mild cases of eczema, individuals may experience occasional itchiness and dryness of the skin. These symptoms can usually be managed with over-the-counter moisturizers and topical creams. However, as eczema progresses and becomes more severe, the symptoms tend to worsen and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Defining Severe Eczema
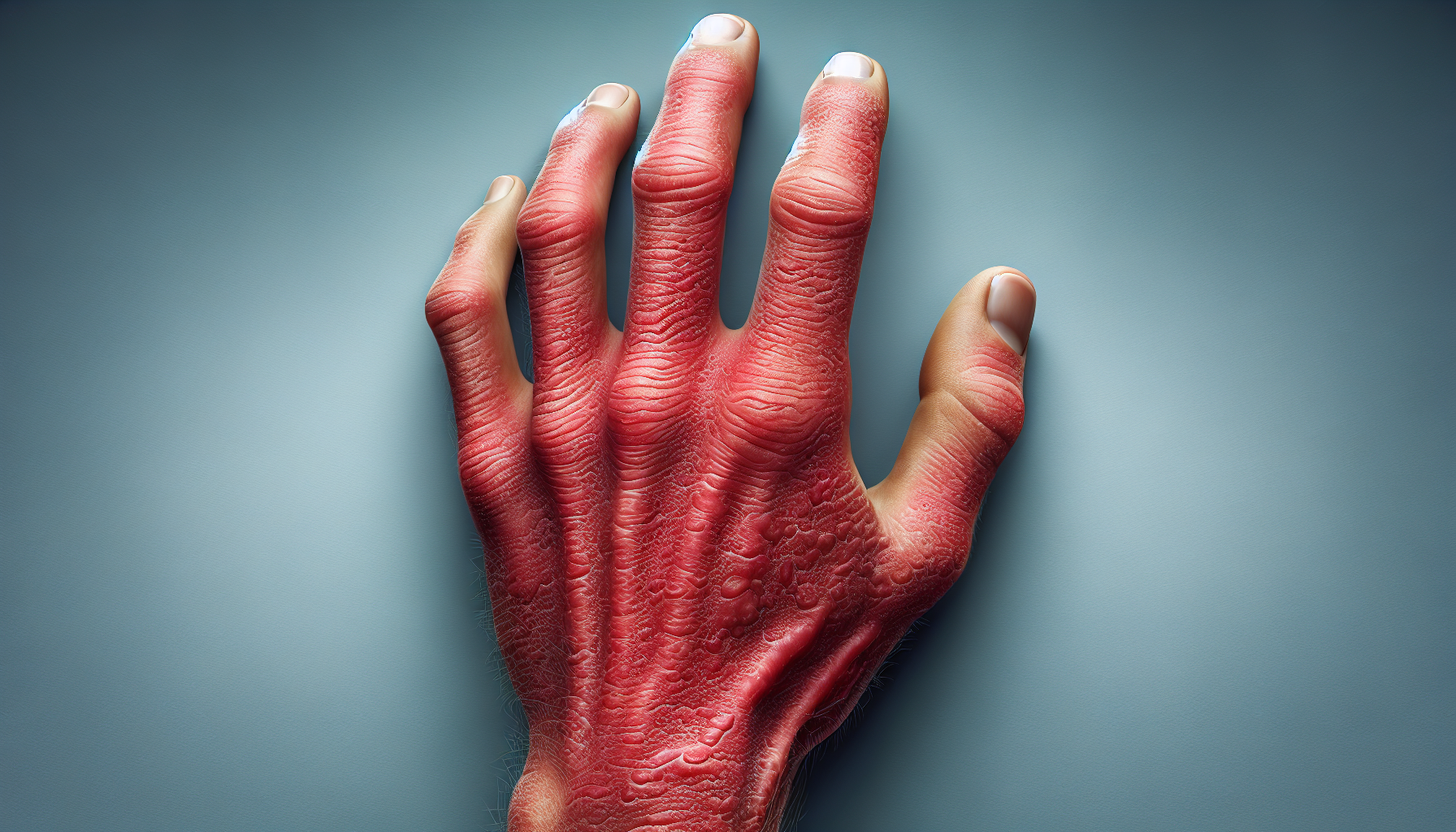
Severe eczema refers to a more intense and persistent form of the condition. It is characterized by severe itching, redness, inflammation, and the presence of thick, scaly skin patches. These symptoms can be present on larger areas of the body and can persist for long periods. Severe eczema may also be resistant to standard treatments and require more intensive interventions.
Characteristics of Severe Eczema
Severe eczema can manifest with various characteristics that differentiate it from milder forms of the condition. These may include:
-
Intense Itching: Severe eczema is often accompanied by relentless itching that can interfere with daily activities and sleep.
-
Extensive Skin Inflammation: The affected areas of skin in severe eczema can be highly inflamed, causing pain and discomfort.
-
Oozing and Crusting: In some cases, severe eczema can result in the discharge of thick, yellowish fluid from the affected areas, leading to crusting and the formation of crusty patches.
-
Skin Thickening and Darkening: Over time, the skin affected by severe eczema can become thicker and darker, making it challenging to manage.
Clinical Diagnosis Criteria
Diagnosing severe eczema involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination by a medical professional. The diagnosis is usually based on the presence of severe symptoms, a significant impact on the individual’s quality of life, and the failure of standard treatments to provide sufficient relief. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other potential causes.
Severity Assessment Tools
To determine the severity of eczema and guide treatment decisions, healthcare professionals may utilize severity assessment tools. These tools involve scoring various aspects of the condition, such as the extent of affected skin, intensity of itching, and overall impact on daily life. By assessing these factors, healthcare providers can gauge the severity of eczema more objectively and tailor treatment accordingly.
Complications of Severe Eczema
Severe eczema not only affects the physical appearance of the skin but can also lead to several complications. Some potential complications of severe eczema include:
-
Secondary Infections: The compromised skin barrier in severe eczema makes individuals more susceptible to bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
-
Sleep Disturbances: The intense itching and discomfort associated with severe eczema can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and diminished quality of life.
-
Emotional Distress: Living with severe eczema can take a toll on one’s mental well-being, leading to feelings of self-consciousness, anxiety, and depression.
-
Impaired Daily Functioning: The visible skin symptoms and associated discomfort can affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities, work, or participate in social events.
Medical Treatments for Severe Eczema
Treating severe eczema often requires a multidimensional approach involving medical interventions. Some common medical treatments for severe eczema include:
-
Topical Steroids: These are potent anti-inflammatory medications that can help reduce inflammation and itching in severe eczema.
-
Immunomodulators: Prescription medications like calcineurin inhibitors can suppress the immune response and alleviate severe eczema symptoms.
-
Systemic Medications: In severe cases, oral or injectable medications such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed to manage symptoms.
-
Biologic Therapies: Recently, biologic therapies that target specific immune pathways involved in eczema have shown promising results in severe cases.
Lifestyle Management for Severe Eczema
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing severe eczema. Some lifestyle management strategies that can help alleviate symptoms include:
-
Moisturization: Regularly applying emollients and moisturizers can help hydrate the skin and prevent dryness, reducing the severity of symptoms.
-
Gentle Skin Care: Individuals with severe eczema should opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic skincare products and avoid harsh soaps and detergents.
-
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as certain foods, allergens, and irritants can help prevent flare-ups in severe eczema.
-
Stress Management: Stress has been known to worsen eczema symptoms. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can help manage severe eczema.
Support and Resources for Severe Eczema Patients
Living with severe eczema can be challenging, but there are support networks and resources available to help individuals cope with the condition. Seeking support from dermatologists, support groups, and online communities can provide valuable insight, encouragement, and guidance on managing severe eczema. Additionally, organizations dedicated to eczema research and advocacy can offer educational resources and raise awareness about the condition.
In conclusion, severe eczema refers to a more intense and persistent form of the condition, characterized by severe itching, inflammation, and the presence of thick, scaly skin patches. Diagnosing the severity of eczema involves a thorough evaluation, and treatment often involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle modifications. By understanding the characteristics, complications, and available support, individuals with severe eczema can take proactive steps towards managing their condition and improving their quality of life.