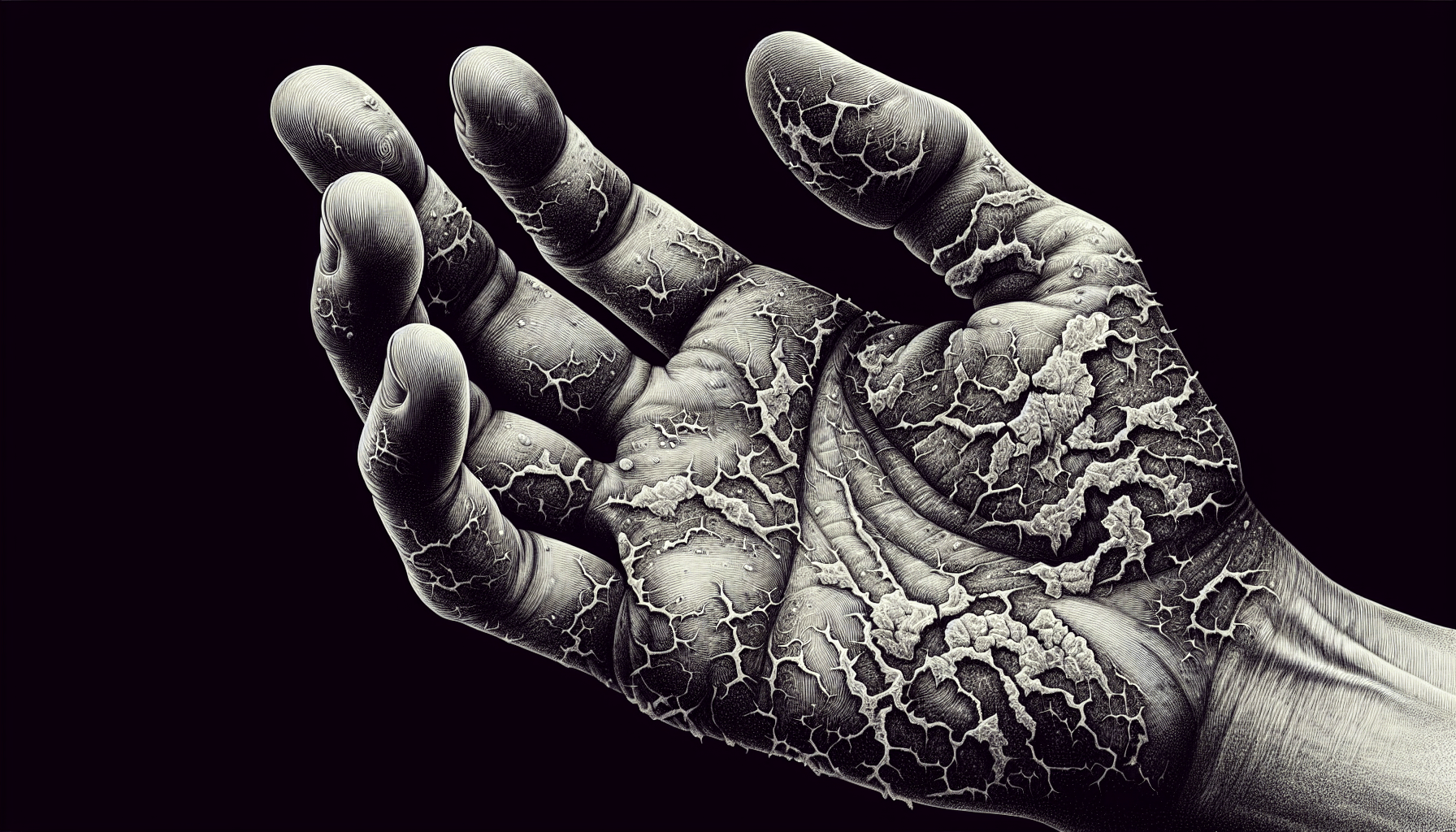
Have you ever wondered about the impact that eczema has on your body? This skin condition, characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed patches, can affect more than just your appearance. Eczema can cause physical discomfort and disrupt your daily life. It is essential to understand the potential damage eczema can do, so you can take the necessary steps to manage and alleviate its effects. In this article, let’s explore the various ways eczema can impact your body and gain insights into how to cope with this condition. Eczema, a common skin condition, can cause various types of damage to the body. From dry and cracked skin to potential complications like scarring and hyperpigmentation, eczema can have a significant impact on an individual’s physical and psychological well-being. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the different ways eczema can affect the body and explore the various symptoms and consequences associated with this condition.
Dry and Cracked Skin
One of the most noticeable effects of eczema is dry and cracked skin. When you have eczema, your skin’s moisture barrier is compromised, leading to excessive dryness. The skin may become rough, itchy, and scaly, causing discomfort and affecting its appearance. Dry and cracked skin is not only visually unappealing but can also lead to further complications, such as skin infections.
Skin Infections
Due to the damaged skin barrier caused by eczema, individuals with this condition are more prone to developing skin infections. Cracks in the skin provide an entry point for bacteria, viruses, and fungi, increasing the risk of infection. Common skin infections associated with eczema include impetigo (a bacterial infection), herpes simplex (eczema herpeticum), and fungal infections like candidiasis. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent these infections from spreading and causing further damage.
Scarring
Severe or chronic eczema can lead to scarring, especially if the skin is repeatedly scratched or injured. The constant scratching can result in deep wounds that heal improperly, leaving behind noticeable scars. These scars may be permanent and can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and body image. Preventing scratching and seeking effective treatment for eczema is essential to minimize the risk of scarring.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation refers to the darkening of the skin, often seen as patches or spots that are darker than the surrounding skin. Eczema can cause hyperpigmentation due to inflammation and damage to the skin cells. After a flare-up subsides, the affected areas may remain darker for an extended period. While hyperpigmentation may fade over time, it can still affect a person’s confidence and self-image.
Discomfort and Pain
Living with eczema can be an uncomfortable and painful experience. The following symptoms commonly accompany this condition:
Itching
Itching is perhaps the most prominent and distressing symptom of eczema. The intense itchiness can be relentless and immensely bothersome, often interfering with daily activities and sleep. Continuous scratching to relieve the itch can exacerbate the condition and increase the risk of infection, making itch management an essential part of eczema treatment.
Burning Sensation
Alongside itching, individuals with eczema may experience a burning sensation on their skin. The affected areas can feel hot and uncomfortable, adding to the overall discomfort associated with the condition. Identifying triggers and implementing measures to reduce inflammation and soothe the skin can help alleviate this burning sensation.
Soreness
Eczema flare-ups can leave the skin feeling sore and tender. The inflamed skin becomes sensitive to touch, making even simple movements and clothing friction painful. Maintaining proper skincare routines, using gentle products, and avoiding irritants can help minimize skin soreness and promote healing.
Swelling
In some cases, eczema can cause localized swelling in the affected areas. Swelling may be a result of the body’s immune response to inflammation. The swollen skin can feel tight and uncomfortable, adding to the physical discomfort experienced by individuals with eczema. Managing inflammation through appropriate skincare and medical treatments can help alleviate swelling.
Sleep Disturbance
Eczema can significantly impact sleep quality, leading to a range of sleep disturbances that affect an individual’s overall well-being. Some common sleep-related issues associated with eczema include:
Difficulty Falling Asleep
The incessant itching and discomfort caused by eczema can make it difficult to fall asleep. The urge to scratch can keep you awake and prevent you from achieving restful sleep. This difficulty in falling asleep can lead to daytime fatigue, reduced productivity, and overall decreased quality of life.
Interrupted Sleep
Even if you manage to fall asleep, eczema-related symptoms can lead to frequent awakenings throughout the night. Itching or discomfort can cause you to wake up multiple times, breaking the sleep cycle and compromising the restorative benefits of deep sleep. Constant interruptions can leave you feeling tired and groggy during the day.
Decreased Sleep Quality
Due to the constant itching, soreness, and other discomforts associated with eczema, sleep quality can be significantly compromised. The lack of deep, uninterrupted sleep can impact physical and mental health, contributing to increased stress, irritability, and other psychological consequences.
Psychological Impact
Eczema’s effects extend beyond the physical realm and can take a toll on your psychological well-being. The following psychological impacts are commonly associated with eczema:
Anxiety
Living with eczema can lead to anxiety, as individuals may constantly worry about flare-ups, appearance, and managing symptoms. The potential for unexpected flare-ups and the fear of social stigma can contribute to heightened anxiety levels. Seeking support from healthcare professionals and engaging in stress management techniques can help alleviate anxiety symptoms.
Depression
The chronic nature and visible appearance of eczema can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and low self-esteem, which may progress to depression. The impact on physical appearance, daily discomfort, and limitations can wear down a person’s mental health over time. Seeking professional help, joining support groups, and practicing self-care strategies can help address and manage depression associated with eczema.
Poor Body Image
Eczema’s visible manifestations, such as dry and scaly skin, sores, and scars, can greatly affect a person’s body image. This can lead to a negative perception of oneself and reduced self-confidence. Engaging in self-acceptance exercises, practicing positive affirmations, and seeking emotional support can aid in improving body image despite the challenges of eczema.
Social Isolation
The physical symptoms and psychological impact of eczema can sometimes lead to social isolation. Individuals may feel self-conscious about their appearance, fear judgment from others, or worry about the potential for contagiousness. As a result, they may withdraw from social activities and relationships. Support networks, therapy, and education about eczema can help overcome social barriers and promote a sense of belonging.
Impaired Physical Function
Eczema can impair an individual’s physical function, making simple daily activities more challenging. The following effects on physical function are commonly associated with this condition:
Limited Range of Motion
Eczema, particularly when it affects joints or areas prone to bending, can limit the range of motion. Inflammation, pain, swelling, and skin tightness can make it difficult to move or flex affected body parts fully. Engaging in appropriate physical exercises, physiotherapy, and joint mobility practices can help maintain or improve range of motion.
Difficulty Performing Daily Activities
Eczema’s physical symptoms can make routine activities demanding and uncomfortable. Simple tasks like showering, dressing, or cooking may become challenging due to sensitivity, discomfort, and the need to carefully manage the affected skin. Identifying practical adaptations or seeking occupational therapy guidance can assist individuals in performing daily activities with greater ease.
Allergic Reactions
Eczema-prone individuals are more susceptible to allergic reactions, including contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. These reactions can occur when the skin comes into contact with irritants or allergens and can range from mild to severe. In addition, individuals with eczema may experience asthma attacks triggered by allergens in the environment. Identifying personal triggers and implementing avoidance strategies or medications prescribed by healthcare professionals can help manage allergic reactions effectively.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with irritants or allergens, leading to redness, itching, and inflammation. Common triggers include certain fabrics, soaps, cosmetics, and cleaning products. Taking precautions such as wearing protective gloves, using mild detergent, and avoiding known irritants can help minimize contact dermatitis and prevent further damage to the skin.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Similar to contact dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis is a specific type of eczematous reaction that occurs when the immune system reacts to an allergen on the skin. The resulting symptoms include redness, swelling, itching, and blisters. Identifying and avoiding allergens through allergy testing, patch testing, and lifestyle adjustments can effectively manage allergic contact dermatitis.
Asthma Attacks
Eczema and asthma often coexist, as both conditions are related to an overactive immune response. Individuals with eczema may experience asthma attacks triggered by environmental allergens, such as pollen, pet dander, or dust mites. Asthma, characterized by wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing, requires appropriate asthma management techniques, including prescribed medications and avoidance of triggers.
Secondary Infections
The compromised skin barrier associated with eczema increases the risk of secondary infections. These infections can result from bacteria, viruses, or fungi entering the broken skin. Common secondary infections seen in individuals with eczema include:
Bacterial Infections
Cracked and open skin provides an entry point for harmful bacteria that can lead to infection. Bacterial infections can manifest as impetigo, cellulitis, folliculitis, or other skin infections. Prompt medical attention, antibiotics, and proper wound care are necessary to treat bacterial infections associated with eczema effectively.
Viral Infections
Herpes simplex, also known as eczema herpeticum, is a viral infection that can occur in individuals with eczema. This infection presents as clusters of painful blisters and requires immediate medical attention. Antiviral medications are typically prescribed to treat herpes simplex and prevent the infection from spreading.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections like candidiasis can occur in areas affected by eczema, particularly where moisture and warmth are trapped. These infections can result in red, itchy rashes and require antifungal medications for effective treatment. Maintaining good hygiene, keeping the skin dry, and avoiding excessive sweating can help prevent fungal infections.
Impact on Quality of Life
Eczema can significantly impact an individual’s overall quality of life. The following factors contribute to the negative effects on daily living:
Disruption of Daily Routine
Managing eczema requires a significant amount of time, attention, and effort. Regular skincare routines, the application of prescribed medications, tracking triggers, and avoiding irritants can disrupt an individual’s daily routine. The constant need to address and manage eczema symptoms can consume time that could be spent on other activities or hobbies.
Emotional Distress
Living with a chronic condition like eczema can lead to emotional distress. The physical discomfort, visible manifestations, and social implications can contribute to feelings of frustration, sadness, and anxiety. Seeking emotional support, practicing self-care, and engaging in stress reduction techniques can help individuals cope with emotional distress linked to eczema.
Reduced Productivity
Due to the physical symptoms of eczema, individuals may experience reduced productivity in their personal and professional lives. The discomfort, pain, itching, and sleep disturbances associated with eczema can make it challenging to concentrate, perform tasks efficiently, and meet deadlines. Implementing strategies like time management, effective communication, and workplace accommodations can help individuals maintain productivity despite the challenges posed by eczema.
Potential Complications
Although rare, certain complications can arise from severe or uncontrolled eczema. These complications require immediate medical attention to prevent further harm. Some potential complications associated with eczema include:
Eczema Herpeticum
Eczema herpeticum is a severe viral infection that occurs when the herpes simplex virus infects the broken skin affected by eczema. It presents as a rapidly spreading rash, often accompanied by flu-like symptoms. Prompt medical intervention, antiviral medications, and proper wound care are necessary to treat eczema herpeticum effectively.
Neurodermatitis
Prolonged and repeated scratching due to eczema can lead to a condition called neurodermatitis. This condition manifests as thick, leathery patches of skin that are intensely itchy. Breaking the scratching cycle, seeking professional help, and using prescribed medications or therapies can manage neurodermatitis effectively.
Eye Complications
Eczema can affect the skin around the eyes, leading to eye complications such as inflammation, redness, itching, and watery eyes. The presence of eczema near the eyes can also increase the risk of developing eye infections. Seeking medical attention from an ophthalmologist and implementing proper eye care routines can help prevent and manage eye complications associated with eczema.
Scarring and Hyperpigmentation
As mentioned earlier, eczema can cause scarring and hyperpigmentation, particularly when the skin is repeatedly scratched or injured. Scarring occurs when wounds heal improperly, leaving behind permanent marks on the skin. Hyperpigmentation, on the other hand, refers to the darkening of the skin in affected areas due to inflammation and damage to the skin cells. While both scarring and hyperpigmentation can impact an individual’s self-image, there are treatment options available to minimize their appearance, such as laser therapy, topical treatments, and skincare routines focused on promoting skin healing.
In conclusion, eczema can cause a range of damage to the body, both physically and psychologically. From dry and cracked skin to potential complications like scarring and infections, eczema can profoundly impact an individual’s quality of life. It is crucial to seek medical attention, follow a comprehensive treatment plan, and practice self-care strategies to manage eczema effectively and minimize its negative effects. Remember, you are not alone in your journey with eczema, and with the right support and treatment, you can navigate the challenges posed by this condition and lead a fulfilling life.